Equity Report
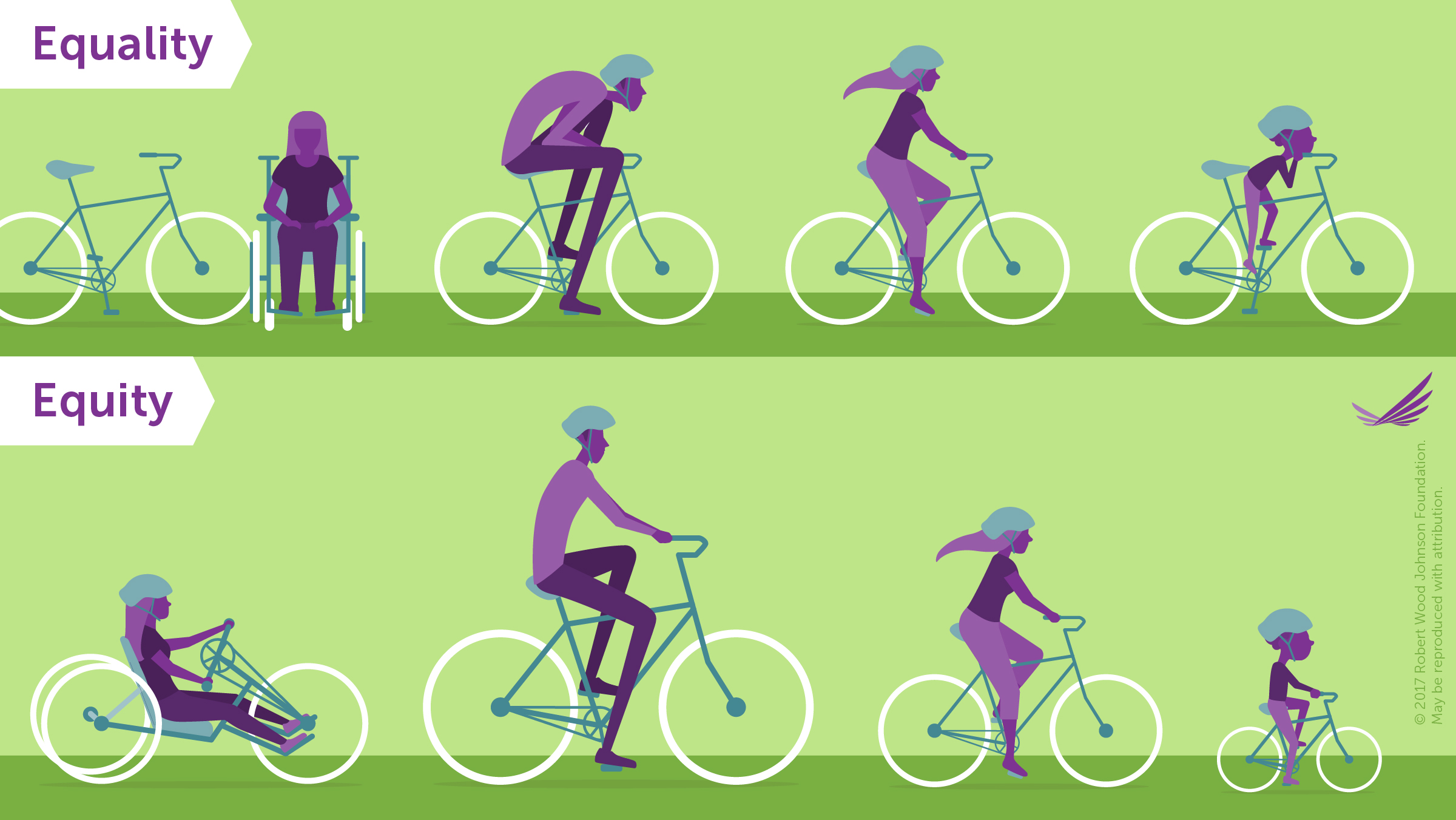
Health Equity implies that ideally everyone would have the same opportunity to reach their full health potential and that no one would be disadvantaged in any way while trying to achieve their entire potential.
Disparity vs Inequity
Though sometimes used interchangeably, disparity and inequity have different definitions. According to Human Impact Partners: health disparities are differences in health status and mortality rates across population groups, which can sometimes be expected, such as cancer rates in the elderly versus children; health inequities are differences in health status and mortality rates across population groups that are systemic, avoidable, unfair, and unjust, such as breast cancer mortality for black women versus white women.

Minority groups in the MiHIA Region are hit especially hard with economic disparities. According to the American Community Survey, for 2015-2019:
Black/African Americans, Hispanic/Latino Americans, and race/ethnicities described as “Other” consistently experience lower Median Household Income and Per Capita Income.
Black individuals in Gratiot County earned on average only $5,294 per person.
Hispanic/Latino households in Clare County have a median household income of $19,992, with 50.2% living below poverty level.
It’s not just minorities who fare tougher economically in the MiHIA Region; children under age 11 are the most common age group to live below the poverty level. Approximately 43% of 6-11-year-olds in Clare County and 35% in Roscommon County live below the poverty line.
*American Community Survey 2015-2019
*American Community Survey 2015-2019
Sharp disparities can be seen in educational attainment in the Region as well. While 20% of residents in the MiHIA Region have earned a Bachelor’s Degree, this is true for only 13.3% of Hispanic/Latinos and 11.1% of Blacks. Arenac County has seen only 51.1% of Black residents graduate high school and 68.7% of Hispanic/Latinos in Sanilac County.
Coronary heart disease (also called coronary artery disease) occurs when the coronary arteries become narrowed or clogged by fat and cholesterol deposits (plaques) and cannot supply enough blood to the heart.
As seen in national trends, men in the MiHIA Region are more likely than women to die from coronary heart disease.
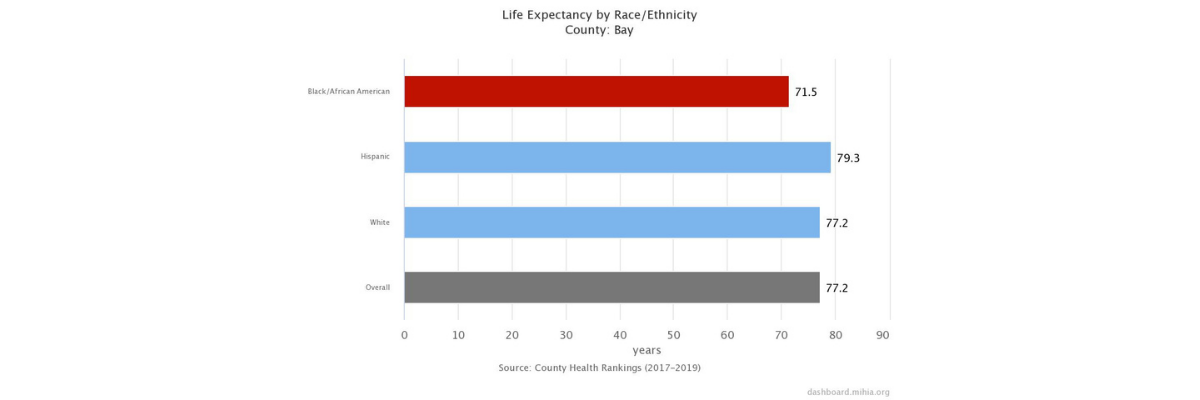
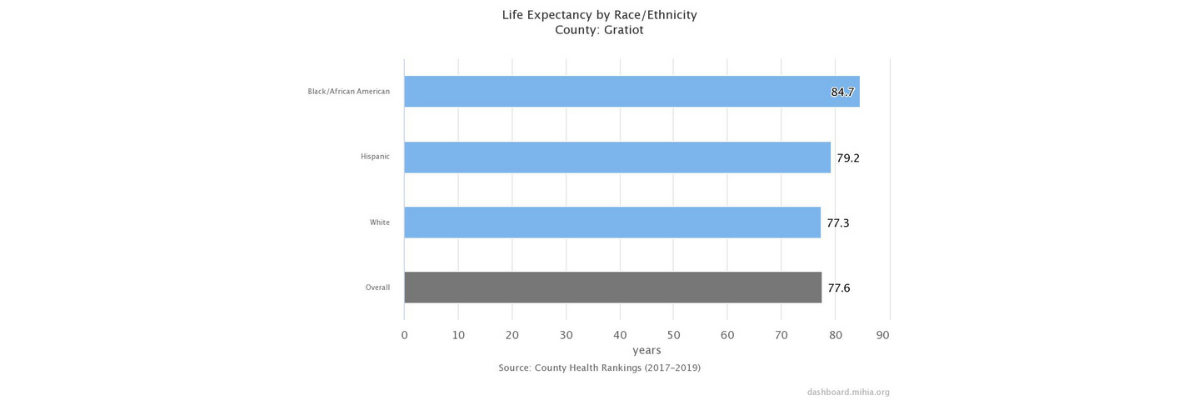
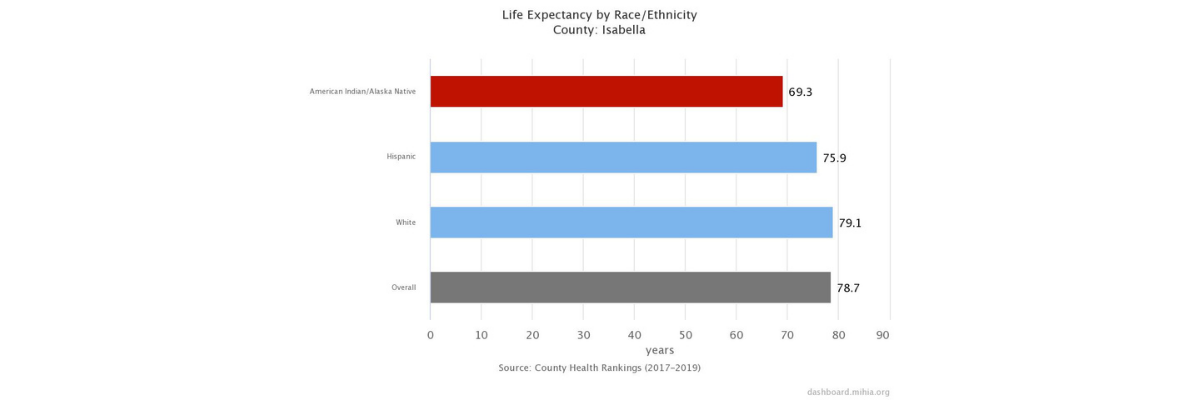
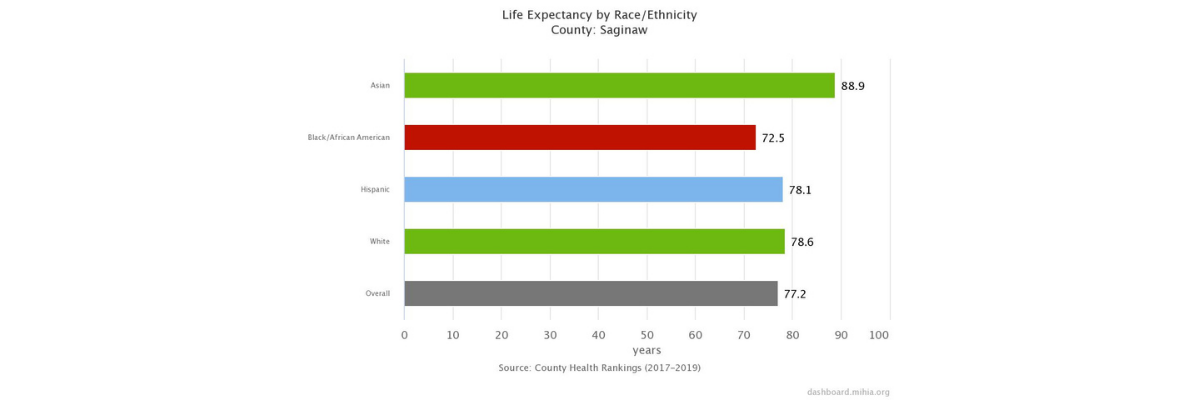
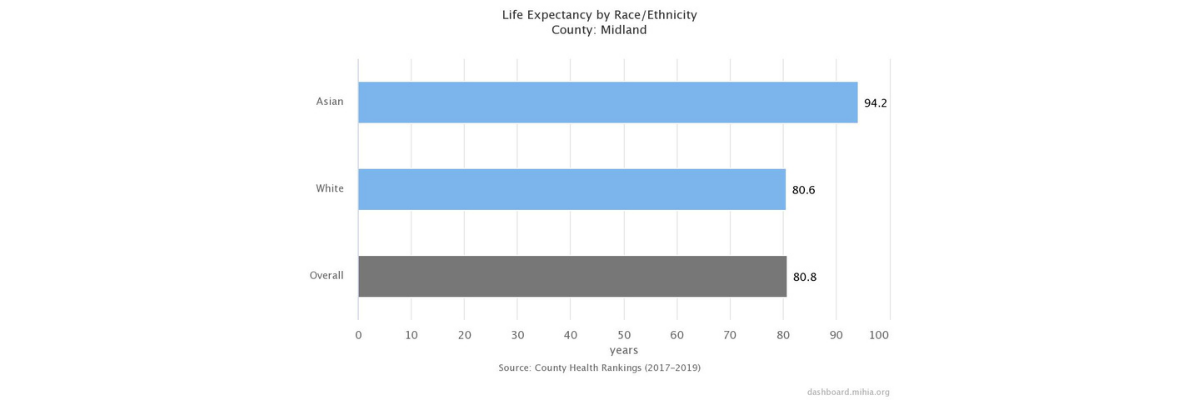
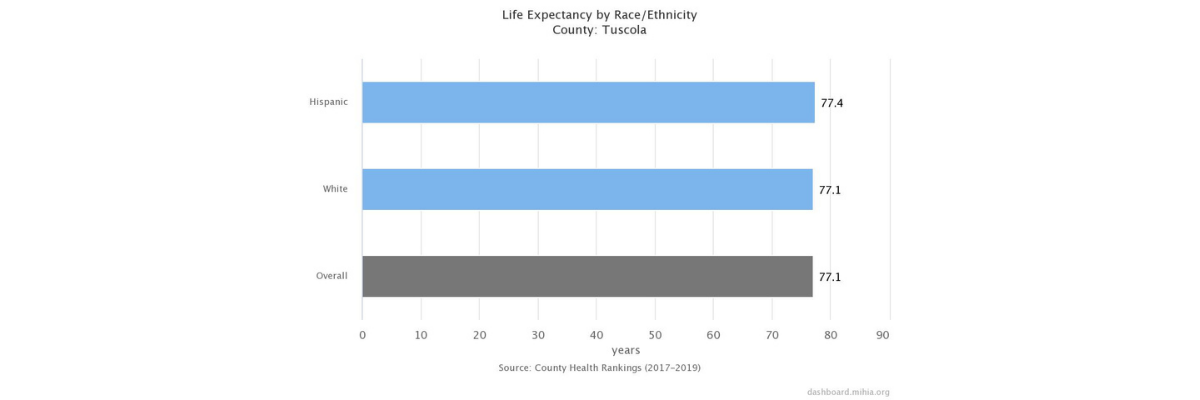
Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is a good measure of a population's longevity and general health. It is highly dependent on infant mortality rates and all-cause death rates. Although the overall U.S. average life expectancy at birth has been steadily increasing, there are great variations in life expectancy between racial and ethnic groups.
Obesity
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, obese children and adolescents are more likely to become obese as adults. Obese and overweight children and adolescents are at risk for multiple health problems during their youth, which are likely to be more severe as adults. Contributing factors to childhood obesity include dietary patterns, physical inactivity, genetics, medication use, and the physical and social environment.
Our health equity efforts include researching indicators on demographics and social environments such as age, race/ethnicity, homelessness, language, socioeconomic measures, employment status and providing educational, healthy living, and inclusive services for all.

 Significantly better than the overall value
Significantly better than the overall value Significantly worse than the overall value
Significantly worse than the overall value