MIHIA's annual Cost of Care report is a high level assessment that aims to measure the cost trends in the region. By analyzing and presenting the best data available, this report serves as a resource to measure the impact of regional efforts to contain health care costs.
Data Sources utilized include the Bureau of Labor Statistics, Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, Michigan Department of Community Health, Kaiser Family Foundation, and local health insurers in the region (e.g. Aetna, Blue Cross, HealthPlus of Michigan), unless otherwise noted.
WHAT IS COST OF CARE?
Cost of Care is comprised of actual costs of providing services related to the delivery of health care, including the costs of procedures and therapies. MiHIA’s Quadruple Aim Cost of Care strategic goal is that the Cost of Care inflation trend for the MiHIA region will not exceed the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
WHY DOES COST OF CARE MATTER?
Efficient and effective health systems and health care delivery across the region promotes growth throughout the community. This includes increased business growth through a stronger workforce, lower absenteeism, and decreased health care costs on employers, state and local budgets, and individuals. Furthermore, the quality of life for citizens in the region is improved with stronger support in the community to control healthcare costs and the enhanced ability to meet tough health reform challenges related to improving quality and cost of care.
WHAT IMPACTS COST OF CARE?
Some factors that impact cost of care include wasteful healthcare spending, such as unnecessary medical tests, high cost of prescription drugs, increases in obesity and chronic health conditions, consolidation of service providers, and an aging population, which will increase the cost of Medicare, Medicaid, and health care, and require increased levels of care, creating demand.
GOAL
MiHIA’s Quadruple Aim Cost of Care strategic goal is that the Cost of Care inflation trend for the MiHIA region will not exceed the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
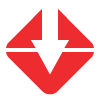
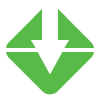
GOAL HAS NOT BEEN MET
4.9%Increase
Cost of Care in MiHIA Region
|
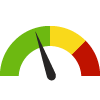
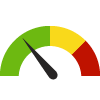
2.3%Increase
Consumer Price Index
|
MiHIA Region Demographics
POPULATION
The population size of a region is used to describe and understand populations and is important in planning for the future of a community, particularly for schools, community centers, health care, and child care.
Access to Care
Health Insurance
Primary Care Provider Rate
Use the dropdown menu to select a location
The Labor Force Participation rate has been steadily declining, most likely due to an aging population
Adults without Health Insurance
Use the dropdown menu to select a location

The medicare population is steadily increasing while the medicaid population rose then dropped
Health Care payments
Uninsured Payments
Employer Paid Coverage & Individual Market Insurance Payments
Region: MiHIA
Medicare Payments
Medicaid Payments
Chronic Conditions
Medicare Population
Chronic Disease Prevalence
Medicaid Population
Chronic Disease Prevalence
Analysis of the differences in the average total cost per beneficiary by the number of claims-based conditions allows for an understanding of the exact financial burden of disease and provides data for more accurate future planning. Some of the claims-based conditions include: Acute Myocardial Infarction, Alzheimer’s Disease, Asthma, Atrial Fibrillation, Cancer, Chronic Kidney Disease, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Depression, Diabetes, Heart Failure, Hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol), Hypertension, Ischemic Heart Disease, Obesity, Osteoporosis, Rheumatoid Arthritis/Osteoarthritis, Schizophrenia, and Stroke.
Medicaid Behavioral Health
Behavioral Health services in Michigan are managed through Community Mental Health Service Programs (CMHSPs) and Prepaid Inpatient Health Plans (PIHPs)
Prepaid Inpatient Health Plan Cases
Mid-State Health Network's total number of PIHP cases are decreasing, while the cost per case ($13,040) is increasing, although still less than the Michigan state average cost
Prepaid Inpatient Health Plan: Mid-State Health Network
Cost of Care Summary
State public health funding per capita is decreasing slightly, while out-of-pocket costs have seen fluctuations
Cost of Care in the MiHIA Region Has Increased Slightly
GOAL HAS NOT BEEN MET
MiHIA’s Quadruple Aim Cost of Care strategic goal is that the Cost of Care inflation trend for the MiHIA region will not exceed the Consumer Price Index (CPI).
| Cost of Care | ||
| Year | Percent Change | Trend |
| 2019 | +4.9% |  |
| 2018 | +4.6% |  |
| 2017 | -2.1% |  |
| 2016 | -5.9% |  |
| 2015 | +4.4% |  |
| 2014 | +3.0% |  |